
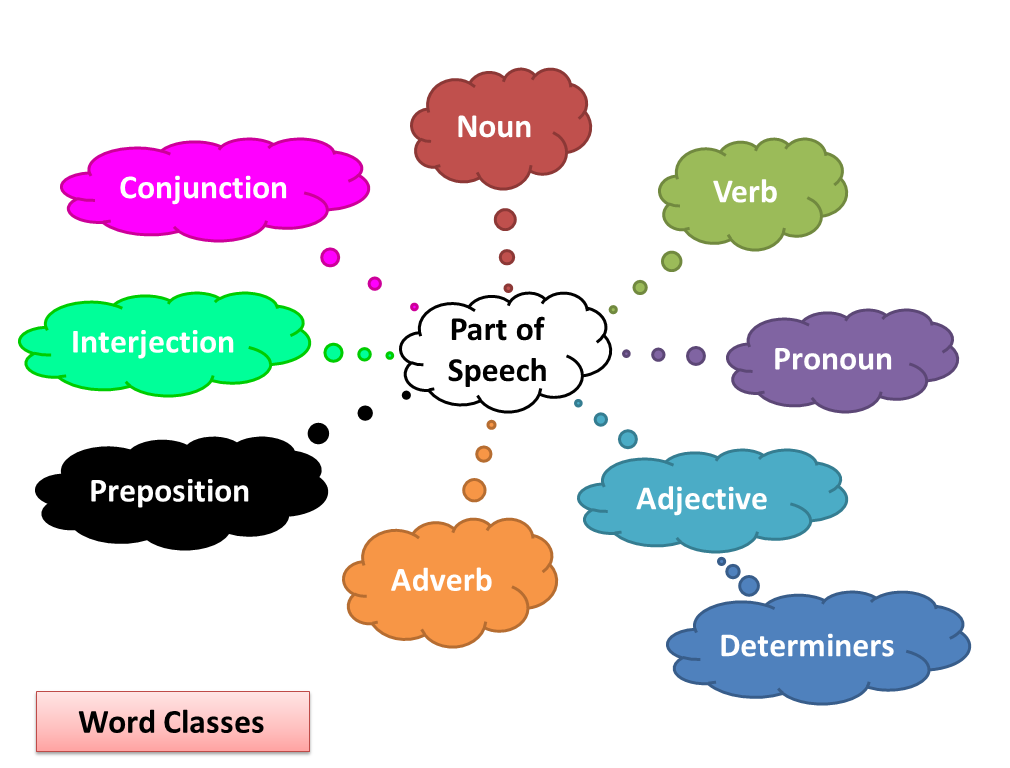
Word classes, also known as parts of speech, are the different categories of words used in grammar. The major word classes are nouns, verbs, adjectives, and adverbs, but there are also minor word classes like prepositions, pronouns, conjunctions, and others. Every word class has its own rules for how it’s used, so knowing a word’s class is important for using it correctly.
- Word classes are divided into two main groups: form and function.
- Form word classes, also known as lexical words, are the most common types of words that make up the important parts of a sentence.
- They include nouns, verbs, adjectives, and adverbs.
- Function word classes, also known as structure words, assist the form word classes in a sentence.
- They include auxiliaries, prepositions, pronouns, determiners, conjunctions, and interjections.
Form word classes:
- noun
- verb
- adjective
- adverb
Function word classes:
- auxiliary
- preposition
- pronoun
- determiner
- conjunction
- interjection
Word class examples
Wow, he has quickly grown into a beautiful cat!
| interjection | pronoun | auxiliary | adverb | verb | preposition | determiner | adjective | noun |
| Wow, | he | has | quickly | grown | into | a | beautiful | cat! |
We will leave early and visit that new museum.
| pronoun | auxiliary | verb | adverb | conjunction | verb | determiner | adjective | noun |
| We | will | leave | early | and | visit | that | new | museum. |
Form word classes
Nouns
Nouns represent people, places, things, or concepts. They can be concrete or abstract; concrete nouns are physical things that can be seen, touched, heard, or otherwise sensed (rocks, noise, grandma), and abstract nouns are nonphysical things that represent ideas (justice, philosophy, happiness).
Examples:
- dog
- pizza
- apple
- The Mandalorian
- Taiwan
Verbs
Verbs represent actions and are the only word class that is absolutely necessary to make a complete sentence. You can conjugate verbs in different verb tenses to explain when an action takes place (past, present, or future) or combine them with auxiliaries for more advanced tenses like the present perfect tense or past continuous tense.
Examples:
- be (is, are, was, were)
- swim
- get
- play
- analyze
Adjectives
Adjectives are words that modify or describe a noun. They add more details to the noun, such as color, size, or age.
Examples:
- big
- green
- ancient
- gorgeous
- difficult
Adverbs
Similar to adjectives, adverbs modify or describe verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs. When describing verbs, they give details about how an action is performed, such as where, when, why, or how often. They usually—but not always—end in -ly.
Examples:
- slowly
- often
- really
- very