Math Lab Activity
– Shaping Up
Objective:
In this activity, you will learn to recognize the characteristics associated with an object, understand the idea of a set, and enhance the logical-thinking skills needed for studying geometry and algebra.
Materials Needed:
- Attribute pieces (buttons, shapes, etc.) with varying attributes (color, shape, size),
- Large pieces of paper
- Pencils.
Instructions:
- Attribute Pieces Sorting:
– Cut out the attribute pieces provided.
– Organize the pieces into piles using 2 colors (for younger students) or 3 colors (for older students).
– Be prepared to explain the reasoning behind your organization.
– Describe the piles you’ve created, such as “I have all the red pieces in this pile” or “I have all the small pieces in this pile.” - Describing Attribute Pieces:
– One student describes an attribute piece, like “This is a small, yellow circle.” - Mystery Block Game:
– Provide a series of clues for the “Mystery Block.”
– Hold up the attribute piece that matches all the clues.
– Continue with a few rounds of this game to challenge your thinking. - Describing Sets:
– Introduce sets: C = {all circles}, R = {all red pieces}, L = {all large pieces}.
– Solve problems together, e.g., “Use words to describe the set C – R.”
– Collect circles, remove red circles, and describe the result, e.g., “C – R = {all yellow and blue circles}.” - Venn Diagram Activity:
– Draw two overlapping circles on a large piece of paper.
– Label one circle “Red” and the other circle “Triangle.”
– Place attribute pieces in the appropriate circle based on their attributes.
– Discuss what goes in the overlapping section (both red and triangle attributes). - Difference Train:
– Create a train of five attribute pieces.
– Each piece should differ from the previous one by only one attribute.
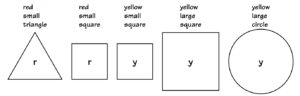
Notice that only one word changes each time.
Example:
1. Use only two colors—yellow and red. There is one piece that fits the clues.
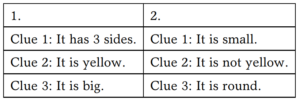
Answers: 1. This piece is a big, yellow triangle. 2. This piece is a small, red circle
Use all three colors—yellow, red, and blue. There are two pieces that fit the clues.
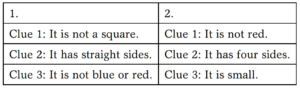
Answers: 1. Small and large yellow triangle. 2. Small, yellow square and small, blue square.
2. Describe in words the following sets.
- L − R = {all large and pieces}
- R − C = {all red and pieces}
- R − L = {all , }
- C − L = {all , }
- L − C = {all large and pieces}
Answers: 1. All large blue and yellow pieces. 2. All red squares and triangles. 3. All small, red pieces. 4. All small circles. 5. All large squares and triangles.
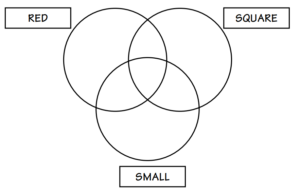
3. Use your attribute pieces and fill in the Venn Diagram shown below.
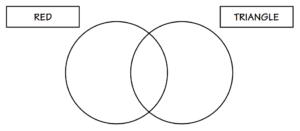
Answer: All small and large red triangles go in the middle intersection. In the left section, there should be all small and large red circles and squares. In the right section, there should be all small and large, yellow, and blue triangles.
Ignite Your Mathematical Mind:
- How can a Venn Diagram be used to represent overlapping relationships among three different sets?
- Can you create a train using five pieces, ensuring that each piece differs by two distinct attributes?
- How could you apply the “Shaping Up” activity using various geometric shapes or a collection of objects, like buttons, each possessing three or more unique attributes?